Active Transport
Active transport (or active uptake) is the mediated transport of biochemicals, and other atomic/molecular substances, across membranes. Unlike passive transport, this process requires the expenditure of cellular energy to move molecules "uphill" against a gradient.
ProcessIn this form of transport, molecules move against either an electrical or concentration gradient (collectively termed an electrochemical gradient).
- The active transport of small molecules or ions across a cell membrane is generally carried out by transport proteins that are found in the membrane.
- Larger molecules such as starch can also be actively transported across the cell membrane by processes known as endocytosis and exocytosis.
- The process whereby particles are moved through a membrane from a region of low concentration to a region of high concentration is known as active transport
Relation to Cellular Energy
Using conservative assumptions, it has been calculated that the amount of energy available to the cell is insufficient to power the estimated degree of active transport, e.g. by a factor of 15-30 times for the sodium pump alone . Following vigorous debate in Science and elsewhere, this discrepancy has yet to be resolved.
Plasmid DNA Extraction

Plasmid is a DNA molecule that is separate from, and can replicate independently of, the chromosomal DNA.[1] They are double stranded and, in many cases, circular. Plasmids usually occur naturally in bacteria, but are sometimes found in eukaryotic organisms .
Plasmids are often used to purify a specific sequence, since they can easily be purified away from the rest of the genome. For their use as vectors, and for molecular cloning, plasmids often need to be isolated.
There are several methods to isolate plasmid DNA from bacteria, the archetypes of which are the miniprep and the maxiprep/bulkprep.The former can be used to quickly find out whether the plasmid is correct in any of several bacterial clones. The yield is a small amount of impure plasmid DNA, which is sufficient for analysis by restriction digest and for some cloning techniques.

In the latter, much larger volumes of bacterial suspension are grown from which a maxi-prep can be performed. Essentially this is a scaled-up miniprep followed by additional purification. This results in relatively large amounts (several micrograms) of very pure plasmid DNA.
Multiple Sclerosis Animation
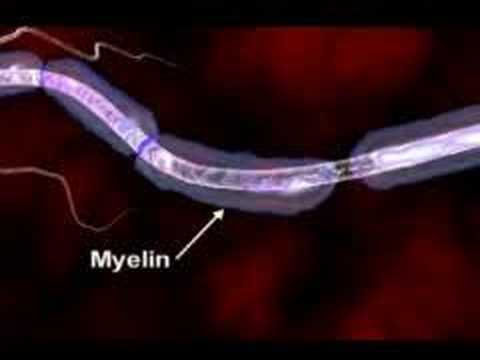
Multiple sclerosis (abbreviated MS, also known as disseminated sclerosis or encephalomyelitis disseminata) is an autoimmune condition in which the immune system attacks the central nervous system, leading to demyelination. Disease onset usually occurs in young adults, and it is more common in women. It has a prevalence that ranges between 2 and 150 per 100,000. MS was first described in 1868 by Jean-Martin Charcot.
MS affects the ability of nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord to communicate with each other. Nerve cells communicate by sending electrical signals called action potentials down long fibers called axons, which are wrapped in an insulating substance called myelin. In MS, the body's own immune system attacks and damages the myelin. When myelin is lost, the axons can no longer effectively conduct signals. The name multiple sclerosis refers to scars (scleroses – better known as plaques or lesions) in the white matter of the brain and spinal cord, which is mainly composed of myelin.Although much is known about the mechanisms involved in the disease process, the cause remains unknown. Theories include genetics or infections. Different environmental risk factors have also been found.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a disease that affects the central nervous system. the CNS which consist of the brain spinal cord optic nerves everything we do whether it's taking a step to solving a problem or simply breathing relies on the proper functioning of the CNS.To understand how MS may impact the CNS we must explore the disease at the cellular level .In the brain millions of nerve cells called neurons continually send and receive signals, each signal is a minute but necessary part of the intricate CNS orchestrations that culminate in the actions, sensations, thoughts and emotions that comprised the human experience.Normally the path over which a nerve signal travels is protected by a type of insulation called the myelin sheath,this insulation is essential for nerve signals to reach their target.In MS the myelin sheath is eroded and the underlying wire like nerve fiber is also damaged, this leads to a breakdown in the ability of the nerve cells transmit signals. it is believed that the loss of myelin is the result of mistaken attack of immune cells.Immune cells protect the body against foreign substances such as bacteria and viruses .But in MS something goes awry.Immune cells infiltrate the brain and spinal cord seek and attack.As ongoing inflammation and tissue damage occurs nerve signals are disrupted. this causes unpredictable symptoms that can range from numbness or tingling to blindness and paralysis.These losses may be temporary or permanent
DNA Extraction
DNA extraction is a routine procedure to collect DNA for subsequent molecular or forensic analysis. There are three basic steps in a DNA extraction:
- Breaking the cells open to expose the DNA within, such as by grinding or sonicating the sample.
- Removing membrane lipids by adding a detergent.
- Precipitating the DNA with an alcohol — usually ethanol or isopropanol. Since DNA is insoluble in these alcohols, it will aggregate together, giving a pellet on centrifugation. This step also removes alcohol-soluble salt.
Refinements of the technique include adding a chelating agent to sequester divalent cations such as Mg2+ and Ca2+. This stops dnase enzymes from degrading the DNA.
Cellular and histone proteins bound to the DNA can be removed prior to its precipitation either by adding a protease or having prior to precipitation, precipitating with sodium or ammonium acetate, or extracting with a phenol-chloroform mixture.
If desired, the DNA can be resolubilized in a slightly alkaline buffer.
Detecting DNA
A diphenylamine (DPA) indicators will confirm the presence of DNA. This procedure involves chemical hydrolysis of DNA: when heated (e.g. ≥95oC) in acid, the reaction requires a deoxyribose sugar and therefore is specific for DNA. Under these conditions, the 2-deoxyribose is converted to w-hydroxylevulinyl aldehyde, which reacts with the compound, diphenylamine, to produce a blue-colored compound. DNA concentration can be determined measuring the intensity of absorbance of the solution at the 600 nm with a spectrophotometer and comparing to a standard curve of known DNA concentrations.
Measuring the intensity of absorbance of the DNA solution at wavelengths 260 nm and 280nm is used as a measure of DNA purity. DNA absorbs UV light at 260 and 280 nm, and aromatic proteins absorbs UV light at 280 nm; a pure sample of DNA has the 260/280 ratio at 1.8 and is relatively free from protein contamination. A DNA preparation that is contaminated with protein will have a 260/280 ratio lower than 1.8.
DNA can be quantified by cutting the DNA with a restriction enzyme, running it on an agarose gel, staining with ethidium bromide or a different stain and comparing the intensity of the DNA with a DNA marker of known concentration.
Using the Southern blot technique this quantified DNA can be isolated and examined further using PCR and RFLP analysis. These procedures allow differentiation of the repeated sequences within the genome. It is these techniques which forensic scientists use for comparison and identification.
Western Blot Animation

The western blot (alternately, immunoblot) is a method of detecting specific proteins in a given sample of tissue homogenate or extract. It uses gel electrophoresis to separate native or denatured proteins by the length of the polypeptide (denaturing conditions) or by the 3-D structure of the protein (native/ non-denaturing conditions). The proteins are then transferred to a membrane (typically nitrocellulose or PVDF), where they are probed (detected) using antibodies specific to the target protein. There are now many reagent companies that specialize in providing antibodies (both monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies) against many thousands of different proteins. Commercial antibodies can be expensive, though the unbound antibody can be reused between experiments. This method is used in the fields of molecular biology, biochemistry, immunogenetics and other mo
Molecular biology disciplines.

Other related techniques include using antibodies to detect proteins in tissues and cells by immunostaining and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The method originated from the laboratory of George Stark at Stanford. The name western blot was given to the technique by W. Neal Burnette and is a play on the name Southern blot, a technique for DNA detection developed earlier by Edwin Southern. Detection of RNA is termed northern blotting.
Steps in a Western blot Tissue preparation
Samples may be taken from whole tissue or from cell culture. In most cases, solid tissues are first broken down mechanically using a blender (for larger sample volumes), using a homogenizer (smaller volumes), or by sonication. Cells may also be broken open by one of the above mechanical methods. However, it should be noted that bacteria, virus or environmental samples can be the source of protein and thus Western blotting is not restricted to cellular studies only. Assorted detergents, salts, and buffers may be employed to encourage lysis of cells and to solubilize proteins. Protease and phosphatase inhibitors are often added to prevent the digestion of the sample by its own enzymes. A combination of biochemical and mechanical techniques – including various types of filtration and centrifugation – can be used to separate different cell compartments and organelles.
Gel electrophoresis
The proteins of the sample are separated using gel electrophoresis. Separation of proteins may be by isoelectric point (pI), molecular weight, electric charge, or a combination of these factors. The nature of the separation depends on the treatment of the sample and the nature of the gel. By far the most common type of gel electrophoresis employs polyacrylamide gels and buffers loaded with sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS). SDS-PAGE (SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis) maintains polypeptides in a denatured state once they have been treated with strong reducing agents to remove secondary and tertiary structure (e.g. S-S disulfide bonds to SH and SH) and thus allows separation of proteins by their molecular weight. Sampled proteins become covered in the negatively charged SDS and move to the positively charged electrode through the acrylamide mesh of the gel. Smaller proteins migrate faster through this mesh and the proteins are thus separated according to size (usually measured in kilo Daltons, kD). The concentration of acrylamide determines the resolution of the gel - the greater the acrylamide concentration the better the resolution of lower molecular weight proteins. The lower the acrylamide concentration the better the resolution of higher molecular weight proteins. Proteins travel only in one dimension along the gel for most blots. Samples are loaded into wells in the gel. One lane is usually reserved for a marker or ladder, a commercially available mixture of proteins having defined molecular weights, typically stained so as to form visible, coloured bands. An example of a ladder is the GE Full Range Molecular weight ladder (Figure 1). When voltage is applied along the gel, proteins migrate into it at different speeds. These different rates of advancement (different electrophoretic mobilities) separate into bands within each lane. It is also possible to use a two-dimensional (2-D) gel which spreads the proteins from a single sample out in two dimensions. Proteins are separated according to isoelectric point (pH at which they have neutral net charge) in the first dimension, and according to their molecular weight in the second dimension.
Transfer
In order to make the proteins accessible to antibody detection, they are moved from within the gel onto a membrane made of nitrocellulose or polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF). The membrane is placed on top of the gel, and a stack of tissue papers placed on top of that. The entire stack is placed in a buffer solution which moves up the paper by capillary action, bringing the proteins with it. Another method for transferring the proteins is called electroblotting and uses an electric current to pull proteins from the gel into the PVDF or nitrocellulose membrane. The proteins move from within the gel onto the membrane while maintaining the organization they had within the gel. As a result of this "blotting" process, the proteins are exposed on a thin surface layer for detection (see below). Both varieties of membrane are chosen for their non-specific protein binding properties (i.e. binds all proteins equally well). Protein binding is based upon hydrophobic interactions, as well as charged interactions between the membrane and protein. Nitrocellulose membranes are cheaper than PVDF, but are far more fragile and do not stand up well to repeated probings. The uniformity and overall effectiveness of transfer of protein from the gel to the membrane can be checked by staining the membrane with Coomassie or Ponceau S dyes. Coomassie is the more sensitive of the two, although Ponceau S's water solubility makes it easier to subsequently destain and probe the membrane as described below.
Blocking
Since the membrane has been chosen for its ability to bind protein, and both antibodies and the target are proteins, steps must be taken to prevent interactions between the membrane and the antibody used for detection of the target protein. Blocking of non-specific binding is achieved by placing the membrane in a dilute solution of protein - typically Bovine serum albumin (BSA) or non-fat dry milk (both are inexpensive), with a minute percentage of detergent such as Tween 20. The protein in the dilute solution attaches to the membrane in all places where the target proteins have not attached. Thus, when the antibody is added, there is no room on the membrane for it to attach other than on the binding sites of the specific target protein. This reduces "noise" in the final product of the Western blot, leading to clearer results, and eliminates false positives.
Detection
During the detection process the membrane is "probed" for the protein of interest with a modified antibody which is linked to a reporter enzyme, which when exposed to an appropriate substrate drives a colourimetric reaction and produces a colour. For a variety of reasons, this traditionally takes place in a two-step process, although there are now one-step detection methods available for certain applications.
Two step
Primary antibody
Antibodies are generated when a host species or immune cell culture is exposed to the protein of interest (or a part thereof). Normally, this is part of the immune response, whereas here they are harvested and used as sensitive and specific detection tools that bind the protein directly. After blocking, a dilute solution of primary antibody (generally between 0.5 and 5 micrograms/ml) is incubated with the membrane under gentle agitation. Typically, the solution is composed of buffered saline solution with a small percentage of detergent, and sometimes with powdered milk or BSA. The antibody solution and the membrane can be sealed and incubated together for anywhere from 30 minutes to overnight. It can also be incubated at different temperatures, with warmer temperatures being associated with more binding, both specific (to the target protein, the "signal") and non-specific ("noise").
Secondary Antibody
After rinsing the membrane to remove unbound primary antibody, the membrane is exposed to another antibody, directed at a species-specific portion of the primary antibody. This is known as a secondary antibody, and due to its targeting properties, tends to be referred to as "anti-mouse," "anti-goat," etc. Antibodies come from animal sources (or animal sourced hybridoma cultures); an anti-mouse secondary will bind to just about any mouse-sourced primary antibody. This allows some cost savings by allowing an entire lab to share a single source of mass-produced antibody, and provides far more consistent results. The secondary antibody is usually linked to biotin or to a reporter enzyme such as alkaline phosphatase or horseradish peroxidase. This means that several secondary antibodies will bind to one primary antibody and enhances the signal. Most commonly, a horseradish peroxidase-linked secondary is used in conjunction with a chemiluminescent agent, and the reaction product produces luminescence in proportion to the amount of protein. A sensitive sheet of photographic film is placed against the membrane, and exposure to the light from the reaction creates an image of the antibodies bound to the blot. As with the ELISPOT and ELISA procedures, the enzyme can be provided with a substrate molecule that will be converted by the enzyme to a colored reaction product that will be visible on the membrane . A third alternative is to use a radioactive label rather than an enzyme coupled to the secondary antibody, such as labeling an antibody-binding protein like Staphylococcus Protein A with a radioactive isotope of iodine. Since other methods are safer, quicker and cheaper this method is now rarely used.
One step
Historically, the probing process was performed in two steps because of the relative ease of producing primary and secondary antibodies in separate processes. This gives researchers and corporations huge advantages in terms of flexibility, and adds an amplification step to the detection process. Given the advent of high-throughput protein analysis and lower limits of detection, however, there has been interest in developing one-step probing systems that would allow the process to occur faster and with less consumables. This requires a probe antibody which both recognizes the protein of interest and contains a detectable label, probes which are often available for known protein tags. The primary probe is incubated with the membrane in a manner similar to that for the primary antibody in a two-step process, and then is ready for direct detection after a series of wash steps.
Analysis
After the unbound probes are washed away, the Western blot is ready for detection of the probes that are labeled and bound to the protein of interest. In practical terms, not all Westerns reveal protein only at one band in a membrane. Size approximations are taken by comparing the stained bands to that of the marker or ladder loaded during electrophoresis. The process is repeated for a structural protein, such as actin or tubulin, that should not change between samples. The amount of target protein is indexed to the structural protein to control between groups. This practice ensures correction for the amount of total protein on the membrane in case of errors or incomplete transfers.
Colorimetric detection
The colorimetric detection method depends on incubation of the Western blot with a substrate that reacts with the reporter enzyme (such as peroxidase) that is bound to the secondary antibody. This converts the soluble dye into an insoluble form of a different color that precipitates next to the enzyme and thereby stains the membrane. Development of the blot is then stopped by washing away the soluble dye. Protein levels are evaluated through densitometry (how intense the stain is) or spectrophotometry.
Chemiluminescence
Chemiluminescent detection methods depend on incubation of the Western blot with a substrate that will luminesce when exposed to the reporter on the secondary antibody. The light is then detected by photographic film, and more recently by CCD cameras which captures a digital image of the Western blot. The image is analysed by densitometry, which evaluates the relative amount of protein staining and quantifies the results in terms of optical density. Newer software allows further data analysis such as molecular weight analysis if appropriate standards are used. So-called "enhanced chemiluminescent" (ECL) detection is considered to be among the most sensitive detection methods for blotting analysis.
Radioactive detection
Radioactive labels do not require enzyme substrates, but rather allow the placement of medical X-ray film directly against the Western blot which develops as it is exposed to the label and creates dark regions which correspond to the protein bands of interest . The importance of radioactive detections methods is declining, because it is very expensive, health and safety risks are high and ECL provides a useful alternative.
Fluorescent detection
The fluorescently labeled probe is excited by light and the emission of the excitation is then detected by a photosensor such as CCD camera equipped with appropriate emission filters which captures a digital image of the Western blot and allows further data analysis such as molecular weight analysis and a quantitative Western blot analysis. Fluorescence is considered to be among the most sensitive detection methods for blotting analysis.
Secondary probing
One major difference between nitrocellulose and PVDF membranes relates to the ability of each to support "stripping" antibodies off and reusing the membrane for subsequent antibody probes. While there are well-established protocols available for stripping nitrocellulose membranes, the sturdier PVDF allows for easier stripping, and for more reuse before background noise limits experiments. Another difference is that, unlike nitrocellulose, PVDF must be soaked in 95% ethanol, isopropanol or methanol before use. PVDF membranes also tend to be thicker and more resistant to damage during use.
2-D Gel Electrophoresis
2-dimensional SDS-PAGE uses the principles and techniques outlined above. 2-D SDS-PAGE, as the name suggests, involves the migration of polypeptides in 2 dimensions. For example, in the first dimension polypeptides are separated according to isoelectric point, while in the second dimension polypeptides are separated according to their molecular weight. The isoelectric point of a given protein is determined by the relative number of positively (e.g. lysine and arginine) and negatively (e.g. glutamate and aspartate) charged amino acids, with negatively charged amino acids contributing to a high isoelectric point and positively charged amino acids contributing to a low isoelectric point. Samples could also be separated first under nonreducing conditions using SDS-PAGE and under reducing conditions in the second dimension, which breaks apart disulfide bonds that hold subunits together. SDS-PAGE might also be coupled with urea-PAGE for a 2-dimensional gel. In principle, this method allows for the separation of all cellular proteins on a single large gel. A major advantage of this method is that it often distinguishes between different isoforms of a particular protein - e.g. a protein that has been phosphorylated (by addition of a negatively charged group). Proteins that have been separated can be cut out of the gel and then analysed by mass spectrometry, which identifies the protein.
Medical diagnostic applications
The confirmatory HIV test employs a Western blot to detect anti-HIV antibody in a human serum sample. Proteins from known HIV-infected cells are separated and blotted on a membrane as above. Then, the serum to be tested is applied in the primary antibody incubation step; free antibody is washed away, and a secondary anti-human antibody linked to an enzyme signal is added. The stained bands then indicate the proteins to which the patient's serum contains antibody. A Western blot is also used as the definitive test for Bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE, commonly referred to as 'mad cow disease'). Some forms of Lyme disease testing employ Western blotting.
Molecular biology disciplines.
Other related techniques include using antibodies to detect proteins in tissues and cells by immunostaining and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The method originated from the laboratory of George Stark at Stanford. The name western blot was given to the technique by W. Neal Burnette and is a play on the name Southern blot, a technique for DNA detection developed earlier by Edwin Southern. Detection of RNA is termed northern blotting.
Steps in a Western blot Tissue preparation
Samples may be taken from whole tissue or from cell culture. In most cases, solid tissues are first broken down mechanically using a blender (for larger sample volumes), using a homogenizer (smaller volumes), or by sonication. Cells may also be broken open by one of the above mechanical methods. However, it should be noted that bacteria, virus or environmental samples can be the source of protein and thus Western blotting is not restricted to cellular studies only. Assorted detergents, salts, and buffers may be employed to encourage lysis of cells and to solubilize proteins. Protease and phosphatase inhibitors are often added to prevent the digestion of the sample by its own enzymes. A combination of biochemical and mechanical techniques – including various types of filtration and centrifugation – can be used to separate different cell compartments and organelles.
Gel electrophoresis
The proteins of the sample are separated using gel electrophoresis. Separation of proteins may be by isoelectric point (pI), molecular weight, electric charge, or a combination of these factors. The nature of the separation depends on the treatment of the sample and the nature of the gel. By far the most common type of gel electrophoresis employs polyacrylamide gels and buffers loaded with sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS). SDS-PAGE (SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis) maintains polypeptides in a denatured state once they have been treated with strong reducing agents to remove secondary and tertiary structure (e.g. S-S disulfide bonds to SH and SH) and thus allows separation of proteins by their molecular weight. Sampled proteins become covered in the negatively charged SDS and move to the positively charged electrode through the acrylamide mesh of the gel. Smaller proteins migrate faster through this mesh and the proteins are thus separated according to size (usually measured in kilo Daltons, kD). The concentration of acrylamide determines the resolution of the gel - the greater the acrylamide concentration the better the resolution of lower molecular weight proteins. The lower the acrylamide concentration the better the resolution of higher molecular weight proteins. Proteins travel only in one dimension along the gel for most blots. Samples are loaded into wells in the gel. One lane is usually reserved for a marker or ladder, a commercially available mixture of proteins having defined molecular weights, typically stained so as to form visible, coloured bands. An example of a ladder is the GE Full Range Molecular weight ladder (Figure 1). When voltage is applied along the gel, proteins migrate into it at different speeds. These different rates of advancement (different electrophoretic mobilities) separate into bands within each lane. It is also possible to use a two-dimensional (2-D) gel which spreads the proteins from a single sample out in two dimensions. Proteins are separated according to isoelectric point (pH at which they have neutral net charge) in the first dimension, and according to their molecular weight in the second dimension.
Transfer
In order to make the proteins accessible to antibody detection, they are moved from within the gel onto a membrane made of nitrocellulose or polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF). The membrane is placed on top of the gel, and a stack of tissue papers placed on top of that. The entire stack is placed in a buffer solution which moves up the paper by capillary action, bringing the proteins with it. Another method for transferring the proteins is called electroblotting and uses an electric current to pull proteins from the gel into the PVDF or nitrocellulose membrane. The proteins move from within the gel onto the membrane while maintaining the organization they had within the gel. As a result of this "blotting" process, the proteins are exposed on a thin surface layer for detection (see below). Both varieties of membrane are chosen for their non-specific protein binding properties (i.e. binds all proteins equally well). Protein binding is based upon hydrophobic interactions, as well as charged interactions between the membrane and protein. Nitrocellulose membranes are cheaper than PVDF, but are far more fragile and do not stand up well to repeated probings. The uniformity and overall effectiveness of transfer of protein from the gel to the membrane can be checked by staining the membrane with Coomassie or Ponceau S dyes. Coomassie is the more sensitive of the two, although Ponceau S's water solubility makes it easier to subsequently destain and probe the membrane as described below.
Blocking
Since the membrane has been chosen for its ability to bind protein, and both antibodies and the target are proteins, steps must be taken to prevent interactions between the membrane and the antibody used for detection of the target protein. Blocking of non-specific binding is achieved by placing the membrane in a dilute solution of protein - typically Bovine serum albumin (BSA) or non-fat dry milk (both are inexpensive), with a minute percentage of detergent such as Tween 20. The protein in the dilute solution attaches to the membrane in all places where the target proteins have not attached. Thus, when the antibody is added, there is no room on the membrane for it to attach other than on the binding sites of the specific target protein. This reduces "noise" in the final product of the Western blot, leading to clearer results, and eliminates false positives.
Detection
During the detection process the membrane is "probed" for the protein of interest with a modified antibody which is linked to a reporter enzyme, which when exposed to an appropriate substrate drives a colourimetric reaction and produces a colour. For a variety of reasons, this traditionally takes place in a two-step process, although there are now one-step detection methods available for certain applications.
Two step
Primary antibody
Antibodies are generated when a host species or immune cell culture is exposed to the protein of interest (or a part thereof). Normally, this is part of the immune response, whereas here they are harvested and used as sensitive and specific detection tools that bind the protein directly. After blocking, a dilute solution of primary antibody (generally between 0.5 and 5 micrograms/ml) is incubated with the membrane under gentle agitation. Typically, the solution is composed of buffered saline solution with a small percentage of detergent, and sometimes with powdered milk or BSA. The antibody solution and the membrane can be sealed and incubated together for anywhere from 30 minutes to overnight. It can also be incubated at different temperatures, with warmer temperatures being associated with more binding, both specific (to the target protein, the "signal") and non-specific ("noise").
Secondary Antibody
After rinsing the membrane to remove unbound primary antibody, the membrane is exposed to another antibody, directed at a species-specific portion of the primary antibody. This is known as a secondary antibody, and due to its targeting properties, tends to be referred to as "anti-mouse," "anti-goat," etc. Antibodies come from animal sources (or animal sourced hybridoma cultures); an anti-mouse secondary will bind to just about any mouse-sourced primary antibody. This allows some cost savings by allowing an entire lab to share a single source of mass-produced antibody, and provides far more consistent results. The secondary antibody is usually linked to biotin or to a reporter enzyme such as alkaline phosphatase or horseradish peroxidase. This means that several secondary antibodies will bind to one primary antibody and enhances the signal. Most commonly, a horseradish peroxidase-linked secondary is used in conjunction with a chemiluminescent agent, and the reaction product produces luminescence in proportion to the amount of protein. A sensitive sheet of photographic film is placed against the membrane, and exposure to the light from the reaction creates an image of the antibodies bound to the blot. As with the ELISPOT and ELISA procedures, the enzyme can be provided with a substrate molecule that will be converted by the enzyme to a colored reaction product that will be visible on the membrane . A third alternative is to use a radioactive label rather than an enzyme coupled to the secondary antibody, such as labeling an antibody-binding protein like Staphylococcus Protein A with a radioactive isotope of iodine. Since other methods are safer, quicker and cheaper this method is now rarely used.
One step
Historically, the probing process was performed in two steps because of the relative ease of producing primary and secondary antibodies in separate processes. This gives researchers and corporations huge advantages in terms of flexibility, and adds an amplification step to the detection process. Given the advent of high-throughput protein analysis and lower limits of detection, however, there has been interest in developing one-step probing systems that would allow the process to occur faster and with less consumables. This requires a probe antibody which both recognizes the protein of interest and contains a detectable label, probes which are often available for known protein tags. The primary probe is incubated with the membrane in a manner similar to that for the primary antibody in a two-step process, and then is ready for direct detection after a series of wash steps.
Analysis
After the unbound probes are washed away, the Western blot is ready for detection of the probes that are labeled and bound to the protein of interest. In practical terms, not all Westerns reveal protein only at one band in a membrane. Size approximations are taken by comparing the stained bands to that of the marker or ladder loaded during electrophoresis. The process is repeated for a structural protein, such as actin or tubulin, that should not change between samples. The amount of target protein is indexed to the structural protein to control between groups. This practice ensures correction for the amount of total protein on the membrane in case of errors or incomplete transfers.
Colorimetric detection
The colorimetric detection method depends on incubation of the Western blot with a substrate that reacts with the reporter enzyme (such as peroxidase) that is bound to the secondary antibody. This converts the soluble dye into an insoluble form of a different color that precipitates next to the enzyme and thereby stains the membrane. Development of the blot is then stopped by washing away the soluble dye. Protein levels are evaluated through densitometry (how intense the stain is) or spectrophotometry.
Chemiluminescence
Chemiluminescent detection methods depend on incubation of the Western blot with a substrate that will luminesce when exposed to the reporter on the secondary antibody. The light is then detected by photographic film, and more recently by CCD cameras which captures a digital image of the Western blot. The image is analysed by densitometry, which evaluates the relative amount of protein staining and quantifies the results in terms of optical density. Newer software allows further data analysis such as molecular weight analysis if appropriate standards are used. So-called "enhanced chemiluminescent" (ECL) detection is considered to be among the most sensitive detection methods for blotting analysis.
Radioactive detection
Radioactive labels do not require enzyme substrates, but rather allow the placement of medical X-ray film directly against the Western blot which develops as it is exposed to the label and creates dark regions which correspond to the protein bands of interest . The importance of radioactive detections methods is declining, because it is very expensive, health and safety risks are high and ECL provides a useful alternative.
Fluorescent detection
The fluorescently labeled probe is excited by light and the emission of the excitation is then detected by a photosensor such as CCD camera equipped with appropriate emission filters which captures a digital image of the Western blot and allows further data analysis such as molecular weight analysis and a quantitative Western blot analysis. Fluorescence is considered to be among the most sensitive detection methods for blotting analysis.
Secondary probing
One major difference between nitrocellulose and PVDF membranes relates to the ability of each to support "stripping" antibodies off and reusing the membrane for subsequent antibody probes. While there are well-established protocols available for stripping nitrocellulose membranes, the sturdier PVDF allows for easier stripping, and for more reuse before background noise limits experiments. Another difference is that, unlike nitrocellulose, PVDF must be soaked in 95% ethanol, isopropanol or methanol before use. PVDF membranes also tend to be thicker and more resistant to damage during use.
2-D Gel Electrophoresis
2-dimensional SDS-PAGE uses the principles and techniques outlined above. 2-D SDS-PAGE, as the name suggests, involves the migration of polypeptides in 2 dimensions. For example, in the first dimension polypeptides are separated according to isoelectric point, while in the second dimension polypeptides are separated according to their molecular weight. The isoelectric point of a given protein is determined by the relative number of positively (e.g. lysine and arginine) and negatively (e.g. glutamate and aspartate) charged amino acids, with negatively charged amino acids contributing to a high isoelectric point and positively charged amino acids contributing to a low isoelectric point. Samples could also be separated first under nonreducing conditions using SDS-PAGE and under reducing conditions in the second dimension, which breaks apart disulfide bonds that hold subunits together. SDS-PAGE might also be coupled with urea-PAGE for a 2-dimensional gel. In principle, this method allows for the separation of all cellular proteins on a single large gel. A major advantage of this method is that it often distinguishes between different isoforms of a particular protein - e.g. a protein that has been phosphorylated (by addition of a negatively charged group). Proteins that have been separated can be cut out of the gel and then analysed by mass spectrometry, which identifies the protein.
Medical diagnostic applications
The confirmatory HIV test employs a Western blot to detect anti-HIV antibody in a human serum sample. Proteins from known HIV-infected cells are separated and blotted on a membrane as above. Then, the serum to be tested is applied in the primary antibody incubation step; free antibody is washed away, and a secondary anti-human antibody linked to an enzyme signal is added. The stained bands then indicate the proteins to which the patient's serum contains antibody. A Western blot is also used as the definitive test for Bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE, commonly referred to as 'mad cow disease'). Some forms of Lyme disease testing employ Western blotting.
Olfactory Pathway Animation
The olfactory system is the sensory system used for olfaction. Most mammals and reptiles have two distinct parts to their olfactory system: a main olfactory system and an accessory olfactory system. The main olfactory system detects volatile, airborn substances, while the accessory olfactory system senses fluid-phase stimuli. Behavioral evidence indicates that most often, the stimuli detected by the accessory olfactory system are pheromones.



The mechanism of the olfactory system can be divided into a peripheral one, sensing an external stimulus and encoding it as an electric signal in neurons, and a central one, where all signals are integrated and processed in the central nervous system.
The olfactory system is often spoken of along with the gustatory system as the chemosensory senses because both transduce chemical signals into perception.
The mechanism of the olfactory system can be divided into a peripheral one, sensing an external stimulus and encoding it as an electric signal in neurons, and a central one, where all signals are integrated and processed in the central nervous system.
In mammals, the main olfactory system detects odorants that are inhaled through the nose, where they contact the main olfactory epithelium, which contains various olfactory receptors. These can distinguish a new odor from the background environmental odors and determine the concentration of the odor.
These olfactory receptors are connected to olfactory receptor neurons in the olfactory epithelium, which transduce receptoractivation into electrical signals in neurons. The signals travel along the olfactory nerve, which belongs to the peripheral nervous system. This nerve terminates in the olfactory bulb, which belongs to the central nervous system.
Using AutoDock
AutoDock is a suite of automated docking tools. It is designed to predict how small molecules, such as substrates or drug candidates, bind to a receptor of known 3D structure.AutoDock actually consists of two main programs: AutoDock performs the docking of the ligand to a set of grids describing the target protein; AutoGrid pre-calculates these grids.In addition to using them for docking, the atomic affinity grids can be visualised. This can help, for example, to guide organic synthetic chemists design better binders.
Autodock Docking
Extracellular signaling
Communication by extracellular signals usually involves six steps: (1) synthesis and (2) release of the signaling molecule by the signaling cell; (3) transport of the signal to the target cell; (4) detection of the signal by a specific receptor protein; (5) a change in cellular metabolism, function, or development triggered by the receptor-signal complex; and (6) removal of the signal, which often terminates the cellular response.

 Subscribe in a reader
Subscribe in a reader
How the NAD+ Works
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, abbreviated NAD+, is a coenzyme found in all living cells. The compound is a dinucleotide, since it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups: with one nucleotide containing an adenosine ring, and the other containing nicotinamide.
In metabolism, NAD+ is involved in redox reactions, carrying electrons from one reaction to another. The coenzyme is therefore found in two forms in cells: NAD+ is an oxidizing agent – it accepts electrons from other molecules and becomes reduced, this reaction forms NADH, which can then be used as a reducing agent to donate electrons. These electron transfer reactions are the main function of NAD+. However, it is also used in other cellular processes, notably as a substrate of enzymes that add or remove chemical groups from proteins, in posttranslational modifications. Due to the importance of these functions, the enzymes involved in NAD+ metabolism are targets for drug discovery.
In organisms, NAD+ can be synthesized from scratch (de novo) from the amino acids tryptophan or aspartic acid. Alternatively, components of the coenzymes are taken up from food as the vitamin called niacin. Similar compounds are released by reactions that break down the structure of NAD+. These preformed components then pass through a salvage pathway that recycles them back into the active form. Some NAD+ is also converted into nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP+); the chemistry of this related coenzyme is similar to that of NAD+, but it has different roles in metabolism.
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide is a dinucleotide since it consists of two nucleotides joined by a pair of bridging phosphate groups. The nucleotides consist of ribose rings, one with adenine attached to the first carbon atom (the 1' position) and the other with nicotinamide at this position. The nicotinamide group can be attached in two orientations to this anomeric carbon atom, due to these two possible structures, the compound exists as two diastereomers. It is the β-nicotinamide diastereomer of NAD+ which is found in organisms. These nucleotides are joined together by a bridge of two phosphate groups through the 5' carbons. In metabolism the compound accepts or donates electrons in redox reactions.Such reactions (summarized in formula below) involve the removal of two hydrogen atoms from the reactant (R), in the form of a hydride ion, and a proton (H+). The proton is released into solution, while the reductant RH2 is oxidized and NAD+ reduced to NADH by transfer of the hydride to the nicotinamide ring. RH2 + NAD+ → NADH + H+ + R From the hydride electron pair, one electron is transferred to the positively-charged nitrogen of the nicotinamide ring of NAD+, and the second hydrogen atom transferred to the C4 carbon atom opposite this nitrogen. The midpoint potential of the NAD+/NADH redox pair is −0.32 volts, which makes NADH a strong reducing agent. The reaction is easily reversible, when NADH reduces another molecule and is re-oxidized to NAD+. This means the coenzyme can continuously cycle between the NAD+ and NADH forms without being consumed. In appearance, all forms of this coenzyme are white amorphous powders that are hygroscopic and highly water-soluble. The solids are stable if stored dry and in the dark. Solutions of NAD+ are colorless and stable for about a week at 4 °C and neutral pH, but decompose rapidly in acids or alkalis. Upon decomposition, they form products that are enzyme inhibitors. Both NAD+ and NADH absorb strongly in the ultraviolet due to the adenine base. For example, peak absorption of NAD+ is at a wavelength of 259 nanometers (nm), with an extinction coefficient of 16,900 M-1cm-1. NADH also absorbs at higher wavelengths, with a second peak in UV absorption at 339 nm with an extinction coefficient of 6,220 M-1cm-1. This difference in the ultraviolet absorption spectra between the oxidized and reduced forms of the coenzymes at higher wavelengths makes it simple to measure the conversion of one to another in enzyme assays – by measuring the amount of UV absorption at 340 nm using a spectrophotometer. NAD+ and NADH also differ in their fluorescence. NADH in solution has an emission peak at 460 nm and a fluorescence lifetime of 0.4 nanoseconds, while the oxidized form of the coenzyme does not fluoresce. The properties of the fluorescence signal changes when NADH binds to proteins, so these changes can be used to measure dissociation constants, which are useful in the study of enzyme kinetics. These changes in fluorescence are also used to measure changes in the redox state of living cells, through fluorescence microscopy.
Monoclonal Antibody for Cancer Treatment
Ron Levy, MD, professor of Medicine at Stanford, recounts his experiences moving his discovery from the lab to the clinical setting and discusses the future of this cancer treatment. Wendy Harpham, a participant in the early clinical trials of Rituxan, the first FDA-approved monoclonal antibody for cancer treatment that Levy developed, provides a patient's perspective.
A Bioinformatics Approach to Clinical Sequencing (Lecture)
Dr. Rhodes has a 12-year track record in cancer genomics and bioinformatics, with a significant focus on building systems to enable cutting-edge cancer research. He founded a successful cancer genomics and informatics company, Compendia Bioscience, recently acquired by Life Technologies. To build Compendia, he recruited and trained a talented team of 30 clinical scientists, bioinformaticists, cancer biologists, data curators and software engineers. As a graduate student, he led the development of Oncomine (Rhodes et al, PNAS, 2004; Rhodes et al, Nature Genetics, 2005), a cancer microarray database and data-mining application. Through the use of Oncomine, he contributed to several important discoveries, including the discovery of gene fusions in prostate cancer (Tomlins, Rhodes, et al., Science, 2005), SPINK1 in prostate cancer (Tomlins, Rhodes et al, Cancer Cell, 2008) and AGTR1 in breast cancer (Rhodes et al, PNAS, 2009). Compendia has since extensively expanded the Oncomine platform, and Oncomine is now widely recognized in academia and pharma as the leading cancer genomics data mining resource, with several hundred citations, and 15,000+ users. As Head of Medical Science Informatics at Life Technologies, he has turned his focus to next-generation sequencing data analysis, and leads several collaborations with pharmaceutical companies aimed at discovering novel oncogenic mutations and gene fusions from thousands of exomes and transcriptomes from The Cancer Genome Atlas. In his role as an Adjunct Assistant Professor at the U. of Michigan, he contributes to cancer genome analyses of prostate cancers (Grasso et al, Nature, 2012) and participates in and advises the clinical sequencing initiative MI-ONCOSEQ. (Ref:Bioconference)
Slides
DNA Fingerprinting Animation

The chemical structure of everyone's DNA is the same. The only difference between people (or any animal) is the order of the base pairs. There are so many millions of base pairs in each person's DNA that every person has a different sequence.
Using these sequences, every person could be identified solely by the sequence of their base pairs. However, because there are so many millions of base pairs, the task would be very time-consuming. Instead, scientists are able to use a shorter method, because of repeating patterns in DNA.
These patterns do not, however, give an individual "fingerprint," but they are able to determine whether two DNA samples are from the same person, related people, or non-related people. Scientists use a small number of sequences of DNA that are known to vary among individuals a great deal, and analyze those to get a certain probability of a match.
These patterns do not, however, give an individual "fingerprint," but they are able to determine whether two DNA samples are from the same person, related people, or non-related people. Scientists use a small number of sequences of DNA that are known to vary among individuals a great deal, and analyze those to get a certain probability of a match.
The Southern Blot is one way to analyze the genetic patterns which appear in a person's DNA. Performing a Southern Blot involves:
1. Isolating the DNA in question from the rest of the cellular material in the nucleus. This can be done either chemically, by using a detergent to wash the extra material from the DNA,or mechanically, by applying a large amount of pressure in order to "squeeze out" the DNA.
2. Cutting the DNA into several pieces of different sizes. This is done using one or more restriction enzymes.
3. Sorting the DNA pieces by size. The process by which the size separation, "size fractionation," is done is called gel electrophoresis. The DNA is poured into a gel, such as agarose, and an electrical charge is applied to the gel, with the positive charge at the bottom and the negative charge at the top. Because DNA has a slightly negative charge, the pieces of DNA will be attracted towards the bottom of the gel; the smaller pieces, however, will be able to move more quickly and thus further towards the bottom than the larger pieces. The different-sized pieces of DNA will therefore be separated by size, with the smaller pieces towards the bottom and the larger pieces towards the top.
4. Denaturing the DNA, so that all of the DNA is rendered single-stranded. This can be done either by heating or chemically treating the DNA in the gel.
5. Blotting the DNA. The gel with the size-fractionated DNA is applied to a sheet of nitrocellulose paper, and then baked to permanently attach the DNA to the sheet. The Southern Blot is now ready to be analyzed.
In order to analyze a Southern Blot, a radioactive genetic probe is used in a hybridization reaction with the DNA in question. If an X-ray is taken of the Southern Blot after a radioactive probe has been allowed to bond with the denatured DNA on the paper, only the areas where the radioactive probe binds will show up on the film. This allows researchers to identify, in a particular person's DNA, the occurrence and frequency of the particular genetic pattern contained in the probe.
variable number tandem repeat
A variable number tandem repeats (VNTR) is a short nucleotide sequence ranging from 14 to 100 nucleotides long that is organized into clusters of tandem repeats, usually repeated in the range of between 4 and 40 times per occurrence. Clusters of such repeats are scattered on many chromosomes. Each variant is an allele and they are inherited codominantly.
Coupled with Polymerase chain reactions, VNTRs have been very effective in forensic crime investigations. When VNTRs are cut out, on either side of the sequence, by restriction enzymes and the results are visualized with a gel electrophoresis, a pattern of bands unique to each individual is produced. The number of times that a sequence is repeated varies between different individuals and between maternal and paternal loci of an individual. The likelihood of two individuals having the same band pattern is extremely improbable. Southern blotting is also used to visualize the repeat numbers on the chromosomes. Once the tandem repeat has been found, identification of possible restriction sites on either side of the repeats are carried out. Using restriction enzymes will break the DNA into the repeat sequences plus a little on each end. The number of repeats will determine the length of the fragment of DNA. The repeat sequence itself can be used as a probe, or if the repeat is not long enough, a sequence from the upstream or downstream side can be used. The probe can either be radioactive or have a biotinylated linker for a fluorescent molecule.
In looking at the VNTR data, two basic principles can be relied on:
Tissue Matching- both VNTR bands must match. If the two samples are from the same individual, he must have exactly the same binding pattern.
Inheritance Matching- the matching bands must follow the rules of inheritance. In matching an individual with his parents, a person must have one band that matches from each parent. If the relationship is further, such as a grandparent, then the matches must be consistent with the relatedness.
VNTR evidence is considered to be exclusionary, which means that a mismatch (or no match at all) sample can be excluded from the genetic relationship of the original sample trying to be matched.
There are two principal families of VNTR: minisatellites and microsatelites. The former are sequences of 11-16 bp repeated 1000 times. They are important because they are highly repetitive and dispersed into the genome. In humans, they are present in 60 autosomic loci and can be examined by digesting the DNA and hybriding with a monolocus probe or with another probe derived from a sequence that is common to each locus. The other members of the VNTR family are the microsatellites or STR (short tandem repeats).They are represented by short sequences of 100-200 bp given by the repetition of 1-6 bp sequences. They cannot be digested, so they are amplified by a multiplex PCR. Parental investigation with these kind of markers are non suitable between consanguineous, because electrophoresis profiles will be very similar. So it is possible to examine only one locus. In this way the system is perfect: one allele derives from the mother and the other one from the father. Microsatellites have many uses: they can be used in forensics, genetic variability and parentage studies.
G-Protein Signal-coupled Intracellular signal Transduction

The cAMP signal transduction contains 5 main characters: stimulative hormone receptor (Rs) or inhibitory hormone receptor (Ri); stimulative regulative G-protein (Gs) or inhibitory regulative G-protein (Gi); Adenylyl cyclase; Protein Kinase A (PKA); and cAMP phosphodiesterase.
The Adenylyl cyclase is a 12-transmembrane glycoprotein that catalyzes ATP to form cAMP with the help of cofactor Mg2+ or Mn2+. The cAMP produced is a second messenger in cellular metabolism and is an allosteric activator to Protein kinase A.
Protein kinase A is an important enzyme in cell metabolism due to its ability to regulate cell metabolism by phosphorylating specific committed enzymes in the metabolic pathway. It can also regulate specific gene expression, cellular secretion, and membrane permeability. The protein enzyme contains two catalytic subunits and two regulatory subunits. When there is no cAMP,the complex is inactive. When cAMP binds to the regulatory subunits, their conformation is altered, causing the dissociation of the regulatory subunits, which activates protein kinase A and allows further biological effects.
Stimulative hormone receptor (Rs) is a receptor that can bind with stimulative signal molecules, while inhibitory hormone (Ri) is a receptor that can bind with inhibitory signal molecules.
Stimulative regulative G-protein is a G protein-linked to stimulative hormone receptor (Rs) and its α subunit upon activation could stimulate the activity of an enzyme or other intracellular metabolism. On the contrary, inhibitory regulative G-protein is linked to an inhibitory hormone receptor and its α subunit upon activation could inhibit the activity of an enzyme or other intracellular metabolism.
The Adenylyl cyclase is a 12-transmembrane glycoprotein that catalyzes ATP to form cAMP with the help of cofactor Mg2+ or Mn2+. The cAMP produced is a second messenger in cellular metabolism and is an allosteric activator to Protein kinase A.
Protein kinase A is an important enzyme in cell metabolism due to its ability to regulate cell metabolism by phosphorylating specific committed enzymes in the metabolic pathway. It can also regulate specific gene expression, cellular secretion, and membrane permeability. The protein enzyme contains two catalytic subunits and two regulatory subunits. When there is no cAMP,the complex is inactive. When cAMP binds to the regulatory subunits, their conformation is altered, causing the dissociation of the regulatory subunits, which activates protein kinase A and allows further biological effects.
cAMP phosphodiesterase is an enzyme that can degrade cAMP to 5'-AMP, which terminates the signal.
Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) is the DNA located in organelles called mitochondria. Most other DNA present in eukaryotic organisms is found in the cell nucleus. Nuclear and mitochondrial DNA are thought to be of separate evolutionary origin, with the mtDNA being derived from the circular genomes of the bacteria that were engulfed by the early ancestors of today's eukaryotic cells. Each mitochondrion is estimated to contain 2-10 mtDNA copies.[1] In the cells of extant organisms, the vast majority of the proteins present in the mitochondria (numbering approximately 1500 different types in mammals) are coded for by nuclear DNA, but the genes for some of them, if not most, are thought to have originally been of bacterial origin, having since been transferred to the eukaryotic nucleus during evolution. In most multicellular organisms, mtDNA is inherited from the mother (maternally inherited).
Mechanisms for this include simple dilution (an egg contains 100,000 to 1,000,000 mtDNA molecules, whereas a sperm contains only 100 to 1000), degradation of sperm mtDNA in the fertilized egg, and, at least in a few organisms, failure of sperm mtDNA to enter the egg. Whatever the mechanism, this single parent (uniparental) pattern of mtDNA inheritance is found in most animals, most plants and in fungi as well. mtDNA is particularly susceptible to reactive oxygen species generated by the respiratory chain due to its close proximity. Though mtDNA is packaged by proteins and harbors significant DNA repair capacity, these protective functions are less robust than those operating on nuclear DNA and therefore thought to contribute to enhanced susceptibility of mtDNA to oxidative damage. Mutations in mtDNA cause maternally inherited diseases and are thought to be a major contributor to aging and age-associated pathology.
In humans (and probably in metazoans in general), 100-10,000 separate copies of mtDNA are usually present per cell (egg and sperm cells are exceptions). In mammals, each circular mtDNA molecule consists of 15,000-17,000 base pairs, which encode the same 37 genes: 13 for proteins (polypeptides), 22 for transfer RNA (tRNA) and one each for the small and large subunits of ribosomal RNA (rRNA). This pattern is also seen among most metazoans, although in some cases one or more of the 37 genes is absent and the mtDNA size range is greater. Even greater variation in mtDNA gene content and size exists among fungi and plants, although there appears to be a core subset of genes that are present in all eukaryotes (except for the few that have no mitochondria at all). Some plant species have enormous mtDNAs (as many as 2,500,000 base pairs per mtDNA molecule) but, surprisingly, even those huge mtDNAs contain the same number and kinds of genes as related plants with much smaller mtDNAs.
G protein receptor
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), comprise a large protein family of transmembrane receptors that sense molecules outside the cell and activate inside signal transduction pathways and, ultimately, cellular responses. G protein-coupled receptors are found only in eukaryotes, including yeast, plants, choanoflagellates, and animals. The ligands that bind and activate these receptors include light-sensitive compounds, odors, pheromones, hormones, and neurotransmitters, and vary in size from small molecules to peptides to large proteins. G protein-coupled receptors are involved in many diseases, but are also the target of around half of all modern medicinal drugs
These proteins receive chemical signals from outside the cell and pass the signal into the cell, so that the cell can respond to the signal. The structures of the endogenous ligands for GPCRs are exceptionally diverse. They include biogenic amines such as norephnephrine and serotonine, peptides, glycoproteins, lipids, nucleotides, ions, and proteases. The sensation of exogenous stimuli, such as light, odors, and taste, is also mediated by this class of receptors. Activation of the receptor causes an effector inside the cell to produce a second signal chemical, which eventually triggers the cell to react to the original external chemical signal.
A ligand, in this case Norepinepherine (NE), binds to the receptor and induces a conformational change. This conformational change activates the a/b complex. The complex is bound to GDP while it is inactive. GTP replaces GDP, thus activating the Alpha subunit. The activated Alpha subunit undergoes a conformational change and activates Adenylate Cyclase. Once the Adenylate Cyclase is activated, it is then able to convert ATP. The products of ATP conversion are c-AMP and two phosphate molecules. c-AMP is a second messenger used in many processes required for cell survival and growth.
What is Endocytosis

Endocytosis is a process whereby cells absorb material (molecules such as proteins) from the outside by engulfing it with their cell membrane. It is used by all cells of the body because most substances important to them are large polar molecules, and thus cannot pass through the hydrophobic plasma membrane. The function of endocytosis is the opposite of exocytosis.
The absorption of material from the outside environment of the cell is commonly divided into two processes: phagocytosis and pinocytosis.
Phagocytosis (literally, cell-eating) is the process by which cells ingest large objects, such as cells which have undergone apoptosis, bacteria, or viruses. The membrane folds around the object, and the object is sealed off into a large vacuole known as a phagosome.
Pinocytosis (literally, cell-drinking) is a synonym for endocytosis. This process is concerned with the uptake of solutes and single molecules such as proteins.
Receptor-mediated endocytosis is a more specific active event where the cytoplasm membrane folds inward to form coated pits. These inward budding vesicles bud to form cytoplasmic vesicles.
Endocytosis pathways
There are three types of endocytosis: namely, macropinocytosis, clathrin-mediated endocytosis, and caveolar endocytosis.
Macropinocytosis is the invagination of the cell membrane to form a pocket which then pinches off into the cell to form a vesicle filled with extracellular fluid (and molecules within it). The filling of the pocket occurs in a non-specific manner. The vesicle then travels into the cytosol and fuses with other vesicles such as endosomes and lysosomes.
Clathrin-mediated endocytosis is the specific uptake of large extracellular molecules such as proteins, membrane localized receptors and ion-channels. These receptors are associated with the cytosolic protein clathrin which initiates the formation of a vesicle by forming a crystalline coat on the inner surface of the cell's membrane.
Caveolae consist of the protein caveolin-1 with a bilayer enriched in cholesterol and glycolipids. Caveolae are flask shaped pits in the membrane that resemble the shape of a cave (hence the name caveolae). Uptake of extracellular molecules are also believed to be specifically mediated via receptors in caveolae.
Clathrin-mediated endocytosis
The major route for endocytosis in most cells, and the best understood, is that mediated by the molecule clathrin. This large protein assists in the formation of a coated pit on the inner surface of the plasma membrane of the cell. This pit then buds into the cell to form a coated vesicle in the cytoplasm of the cell. In so doing, it brings into the cell not only a small area of the surface of the cell but also a small volume of fluid from outside the cell.
Vesicles selectively concentrate and exclude certain proteins during formation and are not representative of the membrane as a whole. AP2 adaptors are multisubunit complexes that performs this function at the plasma membrane. The best understood receptors which are found concentrated in coated vesicles of mammalian cells are the LDL receptor (which removes LDL from the blood circulation), the transferrin receptor (which brings ferric ions bound by transferrin into the cell) and certain hormone receptors (such as that for EGF).
At any one moment, about 2% of the plasma membrane of a fibroblast is made up of coated pits. As a coated pit has a life of about a minute before it buds into the cell, a fibroblast takes up its surface by this route about once every 50 minutes. Coated vesicles formed from the plasma membrane have a diameter of about 100nm and a life time measured in a few seconds. Once the coat has been shed, the remaining vesicle fuses with endosomes and proceeds down the endocytic pathway. The actual budding-in process, whereby a pit is converted to a vesicle, is carried out by clathrin assisted by a set of cytoplasmic proteins which includes dynamin and adaptors such as adaptin.
Coated pits and vesicles were first seen in thin sections of tissue in the electron microscope by Thomas Roth and Keith Porter in 1964. The importance of them for the clearance of LDL from blood was discovered by R. G Anderson, Michael S. Brown and Joseph L. Goldstein in 1976. Coated vesicles were first purified by Barbara Pearse, who discovered the clathrin coat molecule, also in 1976.
Understanding Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar Disorder encompasses a wide spectrum of symptoms and is classified according to the types of mood episodes exhibited, including: manic, hypomanic, major depressive and mixed episodes.
Bipolar I disorder involves a manic or mixed episode in contrast to Bipolar II disorder, which involves at least one major depressive episode and at least one hypomanic episode, but no full manic or mixed episodes.
Bipolar Disorder should be differentiated from Major Depressive Disorder (MDD), which is diagnosed when a patient experiences one or more major depressive episodes without any lifetime episodes of hypomania or mania.
Depicted here is a life chart (or mood chart), which follows the patient's lifetime history of mood episodes. This permits the identification of mood episodes that are the most prevalent and important to prevent.
In this patient, as with many patients with bipolar disorder, depressive episodes become the more prominent aspect of the illness as the person ages.
Several morphometric differences have been observed in the brains of Bipolar Disorder patients relative to healthy subjects.
White matter hyperintensities and reduction in grey matter volume, identified with MRI, have been described in patients with Bipolar Disorder.
Increased ventricular size and decreased frontal cortical area volumes may also be observed in Bipolar Disorder patients.
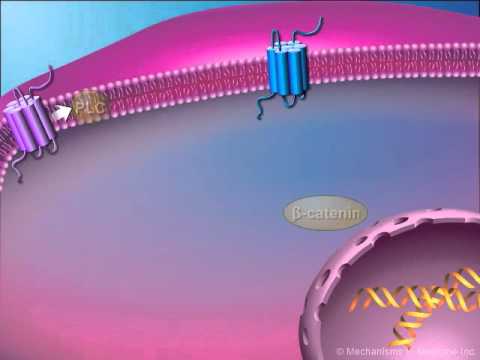
The pathophysiology of Bipolar Disorder encompasses environmental, behavioural, neuronal, cellular, and molecular levels.
At the molecular level, aberrant signaling cascades alter synaptic plasticity. Strong evidence supporting the importance of second messenger signaling has come from studying the targets of mood stabilizing drugs such as lithium.
GSK-3 and IP3 signaling cascades are known to mediate axonogenesis, synaptogenesis, neuronal growth and cone spreading. Other downstream effects may also be involved.
The heritability of bipolar disorder is around 80%. Monozygotic twins are reported to have a higher incidence of developing Bipolar Disorder, approximately 40%, whereas the incidence is only 10% in dizygotic twins.
Although the process of developing bipolar disorder likely arises from complex interactions between genes and environmental factors, the specific genes that contribute to this risk are not known with certainty. Variations of several genes have been identified as potential contributors to the pathophysiology of bipolar disorder.
Among the identified genes are those associated with serotonin signaling (SLC6A4, TPH2), dopamine signaling (SLC6A3, DRD4), glutamate transmission (DAOA, DTNBP1), and cell maintenance and growth (NRG1, BDNF, DISC1).
The most significant environmental triggers of mood episodes among patients with bipolar disorder include use of drugs with mood-altering properties, changes in circadian rhythm, and life stressors.
Successful management of bipolar disorder requires particular attention to minimizing the effects of these influences.
Immunotherapy: Boosting the immune system to fight cancer

The concept of 'teaching' the immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells is over a century old, but the development of immunotherapeutic strategies for cancer was slow for many decades. However, much has been learned about the immune system in the meantime, and with the recent approval of two new immunotherapeutic anticancer drugs and several drugs in late-stage development, a new era in anticancer immunotherapy is beginning.
The video takes an audio-visual journey through the different approaches that are being investigated to harness the immune system to treat cancer.
Nature video on how brain sees
At the micro-scale the brain is a mess; a thick tangle of nerve cells connected at synapses. Mapping just a tiny portion of this mess, a few hundred cells, is a huge challenge. You have to wonder if it's worth the effort. But seeing exactly how brain cells are wired together is giving us new insights into brain function. The researchers who made the 3D maps in this video discovered a new type of cell and worked out how insects see movement. If you've ever tried to swat a fly you'll know how good they are at sensing motion!
Immunology in the Gut Mucosa
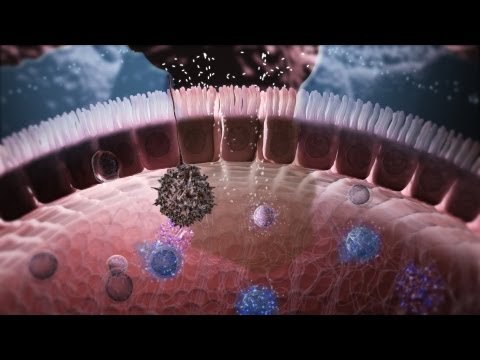
The gut microbiota has an essential role in stimulating the development and maintainance of the intestinal immune system – in fact, without the gut microbiome the human body would be unable to protect its health from being affected by all environmental pathogens that enter the body, e.g. through our daily food. The cellular and molecular mechanisms by which this is achieved are nicely illustrated in a video animation that Nature Immunology has released with the expertise of world-reknown immunologist Tom MacDonald from London:
Fluoroquinolones: Mechanisms of Action and Resistance

In this animation, we demonstrate the biology of DNA replication leading to bacterial cell division in a gram positive bacterium, such as S. pneumoniae. The DNA is shown as a circular double strand within the bacterial cell. Like the DNA of all living organisms, it contains the unique genetic code for all of the proteins required for bacterial survival. Bacteria replicate by a process known as binary fission whereby one bacterium separates into 2 new daughter cells. However, before this can occur, the bacterium must make an identical copy of its complete circular DNA. 
In this animation, we demonstrate the biology of DNA replication leading to bacterial cell division in a gram positive bacterium, such as S. pneumoniae. The DNA is shown as a circular double strand within the bacterial cell. Like the DNA of all living organisms, it contains the unique genetic code for all of the proteins required for bacterial survival. Bacteria replicate by a process known as binary fission whereby one bacterium separates into 2 new daughter cells. However, before this can occur, the bacterium must make an identical copy of its complete circular DNA. DNA replication requires that the two strands of DNA separate so that the genetic code of the bacterium can be read and a new complimentary strand can be created for each of the original strands. To accomplish this, various enzymes known as helicases break the hydrogen bonds between the bases in the two DNA strands, unwind the strands from each other, and stabilize the exposed single strands, preventing them from joining back together. The points at which the two strands of DNA separate to allow replication of DNA are known as replication forks. The enzymes DNA polymerase then move along each strand of DNA, behind each replication fork synthesizing new DNA strands (in red) complementary to the original ones. As the replication forks move forward, positive superhelical twists in the DNA begin to accumulate ahead of them. In order for DNA replication to continue, these superhelical twists must be removed. The bacterial enzyme, DNA gyrase, which is also known as topoisomerase II, is responsible for removing the positive superhelical twists so that DNA replications can procede. DNA gyrase is an essential bacterial enzyme composed of two A and two B subunits which are products of the gyrA and gyrB genes. This enzyme has other important functions which affect the initiation of DNA replication and transcription of many genes. With the combined involvement of these enzymes, an entire duplicate copy of the bacterial genome is produced as the 2 replication forks move in opposite directions around the circular DNA genome. Eventually, as the 2 replication forks meet, 2 new complete chromosomes have been made, each consisting of 1 old and 1 new strand of DNA. This is referred to as semi-conservative replication. In order to allow the 2 new interlinked chromosomes to come apart, another bacterial enzyme is needed which is known as topoisomerase IV. This enzyme is structurally related to DNA gyrase and is coded for by the parC and parE genes. Topoisomerase IV allows for the 2 new inter-linked chromosomes to separate so that they can be segregated into 2 new daughter bacterial cells. Complete separation of bacterial cells Fluoroquinolones. First mechanism of action -- inhibition of DNA gyrase. Fluoroquinolones act by inhibiting the activity of both the DNA gyrase and the topoisomerase IV enzymes. For most gram negative bacteria, DNA gyrase is the primary fluoroquinolone target. Fluoroquinolones have been shown to bind specifically to the complex of DNA gyrase and DNA rather than to DNA gyrase alone. As a result of this binding, quinolones appear to stabilize the enzyme-DNA complexes which in turn results in breaks in the DNA that are fatal to the bacterium. A second mechanism of fluoroquinolone action is shown here. With some exceptions, topoisomerase IV is the primary target of fluoroquinolone action in most gram positive bacteria such as Staphylococci and Streptococci, with DNA gyrase being a secondary target. The separation of 2 new interlinked daughter strands of circular DNA is disrupted. The final result on the bacteria, however, is the same. Bacterial replication is disrupted and the bacterium breaks apart. The relative potency of different fluoroquinolone antibiotics (and thus their spectrum of activity) is dependent in part on their affinity for either DNA gyrase or topoisomerase IV or both. One of the most common mechanisms by which bacteria acquire resistance to fluoroquinolones is by spontaneously occurring mutations in chromosomal genes that alter the target enzymes -- DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV or both. The frequency with which these spontaneous mutations occurs may be in the range of 10-6. The effect of mutations on the activity of an individual fluoroquinolone will vary depending on the number of mutations, the location of the mutations and which target enzyme is affected. If a mutation occurs (either in the gyrA or gyrB gene) that alters DNA gyrase and results in a reduced affinity of the fluoroquinolone antibiotic for this enzyme, the organism will become resistant.
Macrolides: Mechanisms of Action and Resistance
.jpg)
The macrolides are a group of drugs (typically antibiotics) whose activity stems from the presence of a macrolide ring, a large macrocyclic lactone ring to which one or more deoxy sugars, usually cladinose and desosamine, may be attached. The lactone rings are usually 14-, 15-, or 16-membered. Macrolides belong to the polyketide class of natural products.
Antibacterial
Macrolides are protein synthesis inhibitors. The mechanism of action of macrolides is inhibition of bacterial protein biosynthesis, and they are thought to do this by preventing peptidyltransferase from adding the peptidyl attached to tRNA to the next amino acid (similarly to chloramphenicol) as well as inhibiting ribosomal translocation. Another potential mechanism is premature dissociation of the peptidyl-tRNA from the ribosome.
Macrolide antibiotics do so by binding reversibly to the P site on the subunit 50S of the bacterial ribosome. This action is considered to be bacteriostatic. Macrolides tend to accumulate within leukocytes, and are, therefore, transported into the site of infection.
Diffuse panbronchiolitis
The macrolide antibiotics erythromycin, clarithromycin, and roxithromycin have proven to be an effective long-term treatment for the idiopathic, Asian-prevalent lung disease diffuse panbronchiolitis (DPB). The successful results of macrolides in DPB stems from controlling symptoms through immunomodulation (adjusting the immune response), with the added benefit of low-dose requirements.
With macrolide therapy in DPB, great reduction in bronchiolar inflammation and damage is achieved through suppression of not only neutrophil granulocyte proliferation but also lymphocyte activity and obstructive secretions in airways.[6] The antimicrobial and antibiotic effects of macrolides, however, are not believed to be involved in their beneficial effects toward treating DPB. This is evident, as the treatment dosage is much too low to fight infection, and in DPB cases with the occurrence of the macrolide-resistant bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa, macrolide therapy still produces substantial anti-inflammatory results
Resistance
The primary means of bacterial resistance to macrolides occurs by post-transcriptional methylation of the 23S bacterial ribosomal RNA. This acquired resistance can be either plasmid-mediated or chromosomal, i.e., through mutation, and results in cross-resistance to macrolides, lincosamides, and streptogramins (an MLS-resistant phenotype).
Two other types of acquired resistance rarely seen include the production of drug-inactivating enzymes (esterases or kinases), as well as the production of active ATP-dependent efflux proteins that transport the drug outside of the cell.
Azithromycin has been used to treat strep throat (Group A streptococcal (GAS) infection caused by Streptococcus pyogenes) in penicillin-sensitive patients, however macrolide-resistant strains of GAS are not uncommon. Cephalosporin is another option for these patients.
Glioma Cell Death
Glioma is a type of cancer that starts in the brain or spine. It is called a glioma because it arises from glial cells. The most common site of gliomas is the brain.
Symptoms of gliomas depend on which part of the central nervous system is affected. A brain glioma can cause headaches, nausea and vomiting, seizures, and cranial nerve disorders as a result of increased intracranial pressure. A glioma of the optic nerve can cause visual loss. Spinal cord gliomas can cause pain, weakness, or numbness in the extremities. Gliomas do not metastasize by the bloodstream, but they can spread via the cerebrospinal fluid and cause "drop metastases" to the spinal cord.
In this video Non-adherent cell treated with metal colloid based agent to induce apoptosis.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)






.jpg)
.jpg)


